The "Model Method" is a teaching innovation developed in Singapore in the late 1980's. It was developed as a strategy to help students make sense of and solve word problems in the elementary grades. It is a useful strategy for modeling addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, ratios, fractions, percents, and even algebra. (Source: The Singapore Model Method for Learning Mathematics, Ministry of Education, Singapore, 2009)
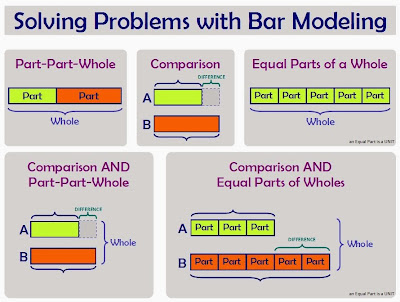
In this method, bars (rectangles) are used to represent quantities in a problem. The length of the bars helps the problem solver visualize the size of the quantities in the problem. The location of the bars relative to each other helps the problem solver visualize how the quantities in the problem are related to each other. Seeing this relationship helps the problem solver decide which operation(s) to use (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) to solve the problem.
The known quantities in the problem are used to label the length of the bars and the unknown quantity is represented by a question mark.
There are three basic structures: Part-Part-Whole, Comparison, and Equal Parts.
The first two, Part-Part-Whole and Comparison, are used when solving simple addition and subtraction situations as described here in the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics.
The third, Equal Parts, is used when solving simple multiplication and division situations as described here in the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics.
For more complex problems, combinations of these simple structures may be used together.
No comments:
Post a Comment